How to Supercharge Your Design Workflow with AI
- 342 shares
- 3 mths ago
Narrow AI, sometimes called Weak AI, encompasses artificial intelligence systems purpose-built for specific, well-defined tasks or applications. These AI systems excel at executing precise functions within a limited scope, and their capabilities remain restricted when compared to human intelligence. Narrow AI can’t generalize its knowledge or skills to tasks beyond its designated domain.
In this video, AI Product Designer Ioana Teleanu defines Narrow AI and the differences between Narrow AI and General AI.
While Narrow AI is tailored for specific tasks, the concept of General AI, or Strong AI, embodies an artificial intelligence system's capability to comprehend, learn, and apply knowledge across a diverse spectrum of tasks, mirroring the adaptability and versatility inherent in human intelligence. Unlike Narrow AI, General AI possesses the potential for advanced reasoning, intricate problem-solving, and the ability to navigate and adapt to novel and unpredictable situations.
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-SA 4.0
Scope of Tasks:
Narrow AI: Specialized in a specific task or set of tasks.
General AI: Capable of performing any intellectual task that a human being can.
Learning and Adaptation:
Narrow AI: Limited to predefined tasks and cannot generalize knowledge.
General AI: Possesses the capacity to learn from experience and apply knowledge to unfamiliar scenarios.
Flexibility:
Narrow AI: Highly specialized and lacks versatility.
General AI: Exhibits adaptability across diverse domains akin to human intelligence.
Narrow AI systems excel within limited scopes, showcasing prowess in executing precise functions. Examples of Narrow AI include:
Voice Recognition Systems: Siri and Alexa demonstrate the application of Narrow AI in seamless human-machine interaction.
Recommendation Algorithms: Streaming services like Netflix and Spotify use Narrow AI to tailor user experiences based on preferences.
Chatbots: These provide customer service assistance on websites, showcasing the efficiency of narrow AI in addressing specific queries.
Specialized Image Recognition Software: Used in facial recognition or medical imaging analysis, which highlights its role in diverse domains.
Fraud Detection Systems: Financial institutions leverage Narrow AI to detect unusual transaction patterns and anomalies, enhancing security measures.
Language Translation Services: Platforms like Google Translate use Narrow AI to provide accurate and context-aware translations, breaking language barriers globally.
Autonomous Vehicles: The automotive industry integrates Narrow AI for tasks such as object recognition and decision-making, contributing to the development of self-driving cars.
In this video, Ioana Teleanu explains how you designers can work with AI as a partner.
Designers have a unique opportunity to harness the power of Narrow AI to create more efficient, personalized, and intuitive user experiences. Here are some ways designers can leverage Narrow AI:
Designers can use Narrow AI to analyze user behavior and preferences, customizing interfaces to provide personalized experiences. This ensures that users receive content and recommendations tailored to their specific needs.
Digital streaming applications like Netflix and Spotify use AI to personalize song and movie recommendations.
© Netflix and Spotify, Fair Use
Implementing Narrow AI in predictive analytics can help designers anticipate user interactions and optimize design elements accordingly. This data-driven approach enhances user satisfaction and engagement.
Zalando employs Narrow AI to predict user preferences and optimize the design layout. By analyzing historical data, the system predicts which products a user will likely be interested in and strategically places them, enhancing the overall user experience.
© Zalando, Fair Use
Integrating AI chatbots into user interfaces can streamline customer support. Designers can ensure that the chatbot's interactions align with the brand's tone and style, providing users with efficient and helpful assistance.
Designers working on AR applications can incorporate Narrow AI's visual recognition capabilities. This enables the application to understand and interact with the user's physical environment, creating immersive and contextually relevant experiences.
AR apps can provide guidance and assist in everyday tasks, like grocery shopping.
© Dent Reality, Fair Use
Narrow AI can analyze user preferences and behavior, facilitating the curation of relevant content. Designers can use this insight to create interfaces that present information that resonates with their user's interests.
Google’s search results page offers contextual information. For example, when you search for a movie, the page will display the show times, a search for a flight will return timings, and a search for a product will return shopping results at the top of the page.
© Google, Fair Use
In design, Narrow AI emerges not just as a technological innovation but as a powerful collaborator, offering designers a myriad of tools and capabilities that enhance and streamline their design process.
In this video, Ioana Teleanu explains how designers can incorporate AI into their processes.
Here's how Narrow AI can be a game-changer for designers:
Insight Generation: Narrow AI can analyze vast datasets, giving designers valuable insights into user behavior, preferences, and trends. This data-driven approach empowers designers to make informed decisions, ensuring their creations align with user expectations. For example, Google Analytics utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze user data, providing designers with insights into user behavior, popular content, and demographic information. Designers can leverage these analytics to inform their design decisions and enhance user experiences.
Time Efficiency: Design often involves repetitive tasks such as resizing images, organizing files, or formatting layouts. Narrow AI can automate these routine activities, allowing designers to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work. This not only boosts efficiency but also minimizes the risk of human error.
Tailored Content: Leveraging Narrow AI enables designers to create personalized user interfaces and content. By understanding user preferences and behaviors, AI-driven designs can dynamically adapt, providing a tailored experience for each user. This personalization enhances user engagement and satisfaction. For example, integrated into Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Sensei automates repetitive design tasks. It can intelligently tag and organize assets, suggest layout adjustments, and even automate complex processes like image masking, saving designers valuable time and effort.
Rapid Prototyping: Narrow AI facilitates rapid prototyping by generating design iterations based on specified parameters. Designers can explore multiple options quickly, accelerating the prototyping phase and fostering a more iterative and experimental design process. For example, Dynamic Yield is an AI-powered personalization platform. Designers can use it to create personalized user interfaces, dynamically adjusting content based on user behavior, preferences, and real-time interactions. For example, RunwayML is a creative toolkit that enables designers to experiment with AI models for rapid prototyping. It provides a range of pre-trained models designers can use to generate visuals, making the prototyping phase more dynamic and exploratory.
Forecasting Aesthetics: Narrow AI can analyze current design trends, predict emerging aesthetics, and even suggest design elements that resonate well with the target audience. This foresight allows designers to stay ahead of the curve and create visually compelling and contemporary designs. For example, IBM Watson Trend uses AI to analyze online trends and predict emerging consumer preferences. Designers can leverage this tool to stay informed about evolving design aesthetics and align their work with current and future trends.
Enhanced Communication: Designers can use Narrow AI equipped with NLP to interpret and understand design briefs expressed in natural language. This improves communication between designers and stakeholders, ensuring a clearer understanding of project requirements and objectives. For example, ChatGPT-3, developed by OpenAI, is a powerful language model that can understand and generate human-like text. Designers can use GPT-3 to interpret and generate design-related text based on natural language input, improving communication with stakeholders.
Inspiration Sourcing: Narrow AI's image recognition capabilities aid designers in sourcing inspiration. AI systems can identify patterns and styles by analyzing visual elements, helping designers stay inspired and informed about evolving design aesthetics. For example, Clarifai is an AI platform that excels in image and video recognition. Designers can use Clarifai to analyze visual elements, identify patterns, and gain inspiration from various styles, streamlining the creative process.
Anticipating Interactions: Narrow AI can analyze user interactions with a design and predict potential user journeys. This anticipatory approach enables designers to optimize user flows, enhancing the designed product's overall user experience and usability. For example, Pendo uses AI to analyze user interactions within digital products. Designers can benefit from insights provided by Pendo to predict and optimize user journeys, ensuring a more intuitive and user-friendly design.
Visual Design: AI algorithms can suggest color palettes and typography combinations based on design principles and user preferences. Designers can experiment with these suggestions, ensuring harmonious and visually appealing compositions. For example, Adobe Color Wheel uses AI algorithms to suggest color palettes based on design principles. Designers can experiment with these suggestions to achieve harmonious color combinations, ensuring visually appealing compositions.
Iterative Improvement: Narrow AI can analyze user feedback on design elements, helping designers understand user sentiment and preferences. This iterative feedback loop allows designers to continuously refine and improve their designs based on real-time user responses. For example, SentiSum employs AI to analyze user feedback and sentiment. Designers can use this tool to understand user responses, identify areas for improvement, and iteratively enhance their designs based on real-time feedback.
As designers embrace the capabilities of Narrow AI, it becomes a valuable collaborator in the creative journey, offering efficiency, innovation, and insights that enrich the design process.
Despite its undeniable advantages, designers must grapple with challenges when incorporating Narrow AI. As a designer, you need to strike a balance between technological innovation and responsible design, which is crucial to navigating the evolving landscape of Narrow AI.
Here are a few tips:
1. Diverse and Representative Data: Ensure that the training data used for Narrow AI models is diverse and representative of the intended user base. This helps mitigate biases and create systems catering to a broad range of users.
2. Bias Detection and Mitigation: Implement tools and methodologies to detect and mitigate biases in the AI algorithms. Regularly review and audit the AI systems to identify and rectify any biased patterns that may emerge during usage.
3. Transparency and Explainability: Design AI systems with transparency in mind. Provide users with understandable explanations of how the AI functions and influences outcomes. This transparency fosters trust and allows users to comprehend the decision-making processes.
4. User Empowerment and Control: Incorporate features that empower users to control and customize AI interactions. This includes settings that allow users to adjust preferences, turn off certain AI features, or provide feedback on the system's performance.
5. Ethical Guidelines and Standards: Adhere to established ethical guidelines and standards in AI development. Stay informed about industry best practices and regulatory frameworks to ensure alignment with ethical principles and legal requirements.
Read the article Bridging the Gap Between Ethics and Practice: Guidelines for Reliable, Safe, and Trustworthy Human-centered AI Systems to learn more about Human-Centered AI.
Learn more about AI and Design in our course AI for Designers.
To learn more about artificial intelligence, read What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Read more about AI and its various applications in the Investopedia article, Artificial Intelligence: What It Is and How It Is Used.
Narrow AI and Weak AI are often used interchangeably to describe a specific type of artificial intelligence, but it's essential to understand their subtle distinctions. Narrow AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that are purpose-built for highly specific tasks or applications. These systems excel at performing well-defined functions within a limited scope, showcasing expertise in a narrow domain.
On the other hand, Weak AI is a broader concept that suggests the limited cognitive abilities of these AI systems compared to human intelligence. The 'weakness' in Weak AI doesn't imply inefficiency but underscores the specificity of the tasks these systems are designed for. In essence, while Narrow AI emphasizes the focused application of AI in a specific domain, Weak AI emphasizes the relative limitation of cognitive abilities compared to the broader spectrum of human intelligence.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
ChatGPT is an example of Narrow AI. It is a sophisticated language model designed for natural language understanding and generation, excelling in conversational contexts. Unlike General AI, which would possess broad cognitive abilities akin to human intelligence across various domains, ChatGPT specializes in processing and generating human-like text based on the input it receives.
ChatGPT’s proficiency is notable within the specific language understanding and generation task, but it cannot generalize its knowledge to a wide range of unrelated tasks. In essence, ChatGPT showcases the capabilities of Narrow AI by demonstrating expertise in a particular domain—in this case, natural language processing.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Siri is a prime example of Narrow AI. As a virtual assistant developed by Apple, Siri is purpose-built for specific tasks related to voice recognition, language understanding, and task execution within the Apple ecosystem.
Siri excels at responding to voice commands, setting reminders, sending messages, and providing information based on user inquiries. However, its capabilities are confined to the predefined set of tasks it is designed for and the Apple ecosystem. Unlike General AI, which would be able to understand and perform a wide array of tasks across diverse domains, Siri's functionality is limited to the specific applications and services integrated into its design.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Alexa is an example of Narrow AI. Developed by Amazon, Alexa is a virtual assistant designed for specific tasks such as voice recognition, natural language processing, and controlling smart home devices. Its capabilities are finely tuned for executing predefined functions, such as providing weather updates, setting reminders, or playing music.
While Alexa exhibits a high level of proficiency within its designated tasks, it operates within a constrained domain and lacks the broad cognitive abilities associated with General AI. In essence, Alexa showcases the characteristics of Narrow AI; it excels in specific applications but doesn’t possess the capacity to generalize knowledge or skills across a wide range of unrelated tasks.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Generative AI and Narrow AI represent different facets of artificial intelligence. Narrow AI, or Weak AI, is tailored for specific tasks within a limited domain, lacking the ability to generalize knowledge. Examples include virtual assistants and specialized algorithms.
Generative AI, on the other hand, refers to systems capable of creating new content, often with the potential for novelty and creativity. While both may operate within specific domains, Narrow AI emphasizes specialized functionality, while Generative AI focuses on content creation.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is a term that characterizes artificial intelligence systems specifically designed and optimized for well-defined tasks or applications. These systems demonstrate expertise within a limited scope, excelling at executing precise functions but lacking the ability to generalize their knowledge or skills to tasks beyond their designated domain. In essence, Narrow AI is highly specialized, showcasing efficiency and accuracy within its predefined boundaries. This stands in contrast to the broader concept of General AI, which encompasses the potential for artificial intelligence to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a diverse spectrum of tasks akin to human intelligence.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Narrow AI, or Weak AI, refers to artificial intelligence systems designed for specific and well-defined tasks or applications. These systems excel within a limited scope, showcasing expertise in executing precise functions tailored to a particular domain. Unlike General AI, Narrow AI cannot generalize its knowledge or skills to tasks beyond its designated focus.
An illustrative example of Narrow AI is voice recognition technology, such as Apple's Siri or Amazon's Alexa. These virtual assistants are meticulously designed to understand and respond to spoken commands, demonstrating proficiency in a narrowly defined area of natural language processing but not possessing the versatility associated with more generalized artificial intelligence.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
A straightforward way to describe Narrow AI is to think of it as specialized artificial intelligence designed for specific tasks. Unlike a versatile, all-encompassing intelligence, Narrow AI excels at performing particular functions within a well-defined domain. It's like having a smart tool that's really good at one job, such as recognizing voices, predicting outcomes based on data, or understanding specific types of images. The essential characteristic is its focused expertise, tailored to handle particular tasks effectively but without the ability to generalize to diverse or unrelated activities.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
An advantage of Narrow or Weak AI lies in its specialized efficiency. Because these artificial intelligence systems are purpose-built for specific tasks or applications, they can demonstrate high performance, accuracy, and speed within their designated domain. This focused expertise allows for the development of highly effective solutions tailored to particular needs. Additionally, the more targeted nature of Narrow AI often makes it more accessible and practical for implementation in real-world scenarios, offering solutions to specific problems without the complexity associated with more generalized artificial intelligence systems.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Narrow AI employs specialized algorithms and models designed for a specific task or application. The process typically involves the following steps:
Task Definition: The first step is defining the specific task or problem the Narrow AI is intended to address. This could range from speech recognition and image classification to data analysis or language translation.
Data Collection: Relevant data for the task is collected and prepared. The quality and diversity of the data play a crucial role in the effectiveness of the Narrow AI system.
Training the Model: The AI model is trained using machine learning techniques, often supervised learning. During training, the model learns patterns and features from the provided data to make accurate predictions or decisions related to the defined task.
Validation and Testing: The trained model is validated and tested using separate datasets to ensure its accuracy, robustness, and generalization to new, unseen data.
Deployment: Once validated, the Narrow AI model is deployed for real-world use. It can then perform the specific task it was designed for recognizing voices, analyzing images, or making predictions based on data.
Iterative Improvement: Continuous improvement is achieved through iterations. The model is refined based on ongoing feedback and new data, enhancing its performance over time.
In essence, Narrow AI works through the application of specialized algorithms to perform a predefined task, leveraging data and iterative learning to optimize its capabilities within that specific domain.
Learn more about AI in the course AI for Designers.
Here’s the entire UX literature on Narrow AI by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Take a deep dive into Narrow AI with our course AI for Designers .
In an era where technology is rapidly reshaping the way we interact with the world, understanding the intricacies of AI is not just a skill, but a necessity for designers. The AI for Designers course delves into the heart of this game-changing field, empowering you to navigate the complexities of designing in the age of AI. Why is this knowledge vital? AI is not just a tool; it's a paradigm shift, revolutionizing the design landscape. As a designer, make sure that you not only keep pace with the ever-evolving tech landscape but also lead the way in creating user experiences that are intuitive, intelligent, and ethical.
AI for Designers is taught by Ioana Teleanu, a seasoned AI Product Designer and Design Educator who has established a community of over 250,000 UX enthusiasts through her social channel UX Goodies. She imparts her extensive expertise to this course from her experience at renowned companies like UiPath and ING Bank, and now works on pioneering AI projects at Miro.
In this course, you’ll explore how to work with AI in harmony and incorporate it into your design process to elevate your career to new heights. Welcome to a course that doesn’t just teach design; it shapes the future of design innovation.
In lesson 1, you’ll explore AI's significance, understand key terms like Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Generative AI, discover AI's impact on design, and master the art of creating effective text prompts for design.
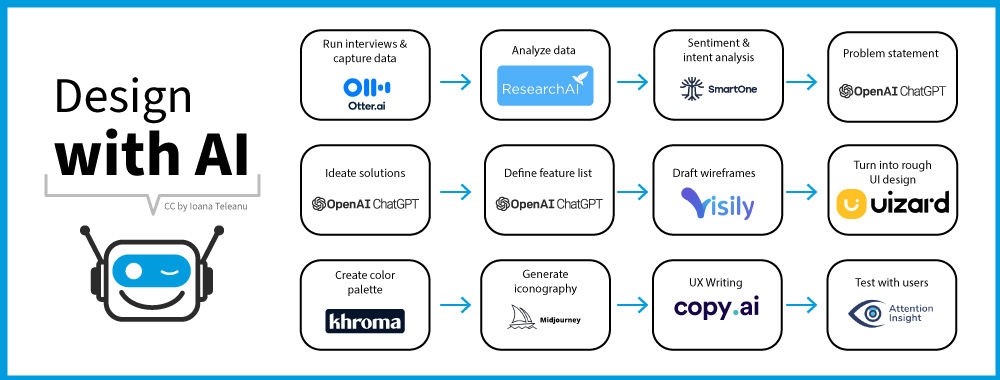
In lesson 2, you’ll learn how to enhance your design workflow using AI tools for UX research, including market analysis, persona interviews, and data processing. You’ll dive into problem-solving with AI, mastering problem definition and production ideation.
In lesson 3, you’ll discover how to incorporate AI tools for prototyping, wireframing, visual design, and UX writing into your design process. You’ll learn how AI can assist to evaluate your designs and automate tasks, and ensure your product is launch-ready.
In lesson 4, you’ll explore the designer's role in AI-driven solutions, how to address challenges, analyze concerns, and deliver ethical solutions for real-world design applications.
Throughout the course, you'll receive practical tips for real-life projects. In the Build Your Portfolio exercises, you’ll practise how to integrate AI tools into your workflow and design for AI products, enabling you to create a compelling portfolio case study to attract potential employers or collaborators.


We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge. Unfortunately, world class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change, , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge!
